13. Running WordPress & Database Containers on Portenta X8
Learn how to run a database and WordPress container on the Portenta X8
Overview
The Arduino Portenta X8's robust features are ideally complemented by Docker containers, simplifying various applications. This tutorial demonstrates how to deploy a WordPress web server on the Portenta X8, leveraging containers for web service and database management.
You will learn to set up and access a WordPress site hosted on the X8 via a web browser.
Goals
- Prepare the necessary files for Docker container deployment
- Deploy and activate the Docker containers on the Portenta X8
- Access and configure the WordPress site hosted on the Portenta X8
Required Hardware and Software
- Portenta X8
- USB-C® cable (either USB-C® to USB-A or USB-C® to USB-C®)
- The docker-compose.yml file used in this tutorial
Instructions
Begin by ensuring your Portenta X8 is ready for use, following the setup guide in the User Manual's Out-of-the-Box Experience.
Creating the docker-compose.yml File
Our WordPress setup involves a multi-container approach, integrating both the WordPress and a MariaDB database server containers. The WordPress container uses Apache as the web server, merged within the container for easy deployment.
To direct this setup, we will craft a docker-compose.yml file describing the configurations for both WordPress and MariaDB containers, including essential settings like usernames, passwords, time zones, and database names. For security, ensure the default passwords are substituted with stronger alternatives in the provided configuration template.
Complete docker-compose.yml File
In this section, you can find the complete docker-compose.yml file that we will be using for this tutorial.
1version: "3.9"2 3services:4 db:5 image: mariadb:latest6 container_name: mariadb7 environment:8 - PUID=10009 - PGID=100010 - MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=Wordpress11 - TZ=Europe/London12 - MYSQL_DATABASE=Wordpress13 - MYSQL_USER=Wordpress14 - MYSQL_PASSWORD=Wordpress15 volumes:16 - db_data:/var/lib/mysql17 restart: unless-stopped18 19 Wordpress:20 depends_on:21 - db22 image: wordpress:latest23 volumes:24 - Wordpress_data:/var/www/html25 ports:26 - "8000:80"27 restart: always28 environment:29 WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db30 WORDPRESS_DB_USER: Wordpress31 WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: Wordpress32 WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: Wordpress33volumes:34 Wordpress_data: {}35 db_data: {}Now, let's prepare our Portenta X8 by creating a directory for our docker-compose.yml file, which can be downloaded here.
Installing The Containers
Begin by creating a directory for the Docker setup, naming it wordpress-test. Navigate into this directory and either copy the docker-compose.yml file into it or create the file directly within.
To create the file on the device, use
, paste the contents, and exit with cat > docker-compose.yml
CTRL + C<path to docker-compose.yml file>1adb push <path to docker-compose.yml file> /home/fio/wordpress-testAlternatively, you could place the
docker-compose.ymlwordpress-testAlternatively, if the docker-compose.yml is already inside the wordpress-test directory on your computer, use:
1adb push .\wordpress-test\ /home/fioChoose the method that best suits your workflow.
Access Docker with administrative privileges by executing
, with sudo su -
as the default password.fio
Ensure no conflicting containers are running on your intended ports by inspecting current containers with
. Remove any active containers by first stopping them with:docker ps -a
1docker stop <container id>Then removing them with:
1docker rm <container id>If you want more information about handling containers on your Portenta X8, take a look at our Managing Containers with Docker tutorial.
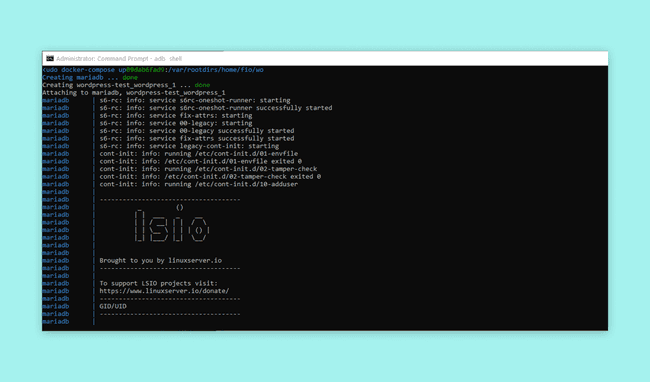
With the setup directory ready and no port conflicts, begin the container installation with:
1docker compose up -dThe
-dThe installation of the WordPress and MariaDB containers will begin and may take some time. To monitor the installation process, use:
1docker-compose logs -fUpon completion, your WordPress site will be accessible from the Portenta X8.
Connecting to the WordPress Site
Accessing your WordPress site on the Portenta X8 is straightforward. Use the following URL format, composed with your Portenta X8's unique id and port, in your browser:
1http://portenta-x8-<uuid>.local:<port>Replace
with your Portenta X8's unique identifier and <uuid>
with the port you have allocated for the WordPress container. You can find your device's <port>
in the setup guide within the User Manual's Out-of-the-Box Experience, through terminal commands involving <uuid>
, or by visiting adb
on Windows and Linux (use http://192.168.7.1:8000
for MacOS).http://192.168.8.1:8000
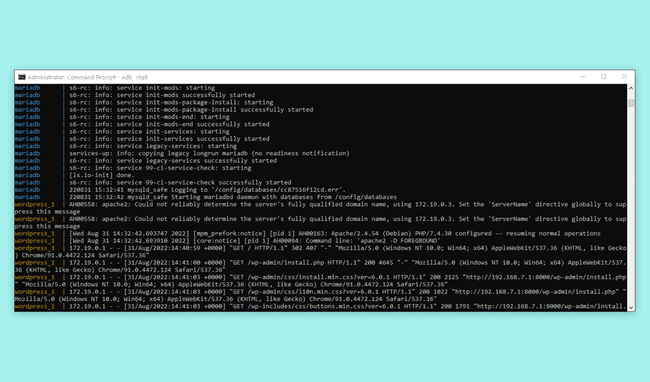
Upon establishing a connection, your terminal will display details similar to those below.
Your browser will then present the WordPress setup page, allowing you to commence the configuration process.
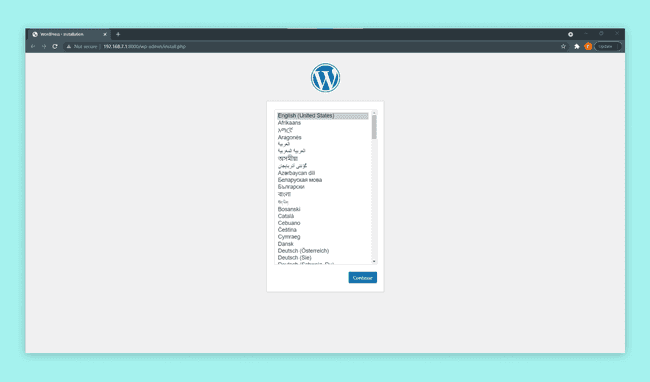
You are now free to go through the WordPress setup process and configure it however you like.
Removing the Containers
Should you need to remove the containers, navigate back to the
directory and use the commands below based on your requirements./home/fio/wordpress-test
To remove the containers while retaining your WordPress data:
1docker compose downTo delete both the containers and all associated data:
1docker compose down --volumesConfirm the removal by executing
and verifying that the WordPress and MariaDB containers are no longer listed.docker ps -a
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we went through installing and running a WordPress and database container on the Portenta X8. We then accessed the WordPress site on our X8 through our web browser. Now, you can set up your WordPress site on your X8 device and access it from another device.
Troubleshooting
If the containers are not being installed or running correctly, check if any other containers are currently running on the same ports as the ones used by the WordPress container. You can check it with
.docker ps -aIf there is any issue running docker commands, ensure you are using
before the commands or having root access using:sudo
with password:sudo su -r
.fioIf you cannot connect to the site when everything is running, you can double-check the X8's IP address. Run the command
in the adb shell. This will display the X8's IP address via USB and Wi-Fi®. Try connecting via those IP addresses if all the rest fails.ip -h address
Suggest changes
The content on docs.arduino.cc is facilitated through a public GitHub repository. If you see anything wrong, you can edit this page here.
License
The Arduino documentation is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 license.